

Jun . 24, 2024 01:21 Back to list
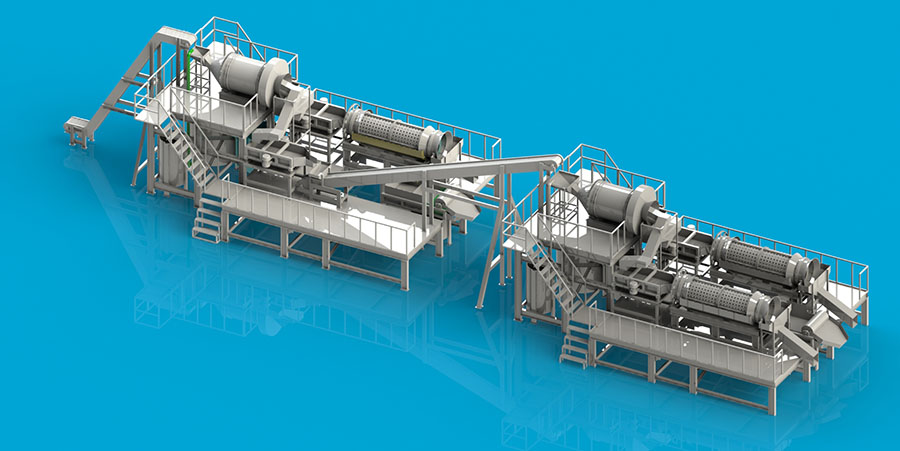 It involves heating PCBs in an oxygen-free environment to break down the polymers into gas, liquid, and char It involves heating PCBs in an oxygen-free environment to break down the polymers into gas, liquid, and char
It involves heating PCBs in an oxygen-free environment to break down the polymers into gas, liquid, and char It involves heating PCBs in an oxygen-free environment to break down the polymers into gas, liquid, and char how to dispose of printed circuit boards. This process recovers valuable metals and produces fuel from the syngas. Despite its potential, pyrolysis requires specialized equipment and energy input, making it less accessible for some recyclers.
Bio-recycling is an emerging technology that uses microorganisms to leach out metals from PCBs. This environmentally friendly process is still under research but presents a promising solution for the future. It aims to minimize chemical use and lower energy consumption compared to other methods.
Physical recycling involves shredding and sorting PCBs to recover metals through mechanical processes. Although simple and straightforward, this method may not retrieve all valuable materials and often requires subsequent chemical or thermal treatments for complete metal extraction.
In conclusion, the disposal of printed circuit boards should prioritize environmental protection and resource recovery. Methods such as incineration, chemical recycling, pyrolysis, bio-recycling, and physical recycling each have their advantages and limitations. As technology continues to advance, so should our approaches to PCB disposal, ensuring a balance between electronic innovation and ecological stewardship.
how to dispose of printed circuit boards. This process recovers valuable metals and produces fuel from the syngas. Despite its potential, pyrolysis requires specialized equipment and energy input, making it less accessible for some recyclers.
Bio-recycling is an emerging technology that uses microorganisms to leach out metals from PCBs. This environmentally friendly process is still under research but presents a promising solution for the future. It aims to minimize chemical use and lower energy consumption compared to other methods.
Physical recycling involves shredding and sorting PCBs to recover metals through mechanical processes. Although simple and straightforward, this method may not retrieve all valuable materials and often requires subsequent chemical or thermal treatments for complete metal extraction.
In conclusion, the disposal of printed circuit boards should prioritize environmental protection and resource recovery. Methods such as incineration, chemical recycling, pyrolysis, bio-recycling, and physical recycling each have their advantages and limitations. As technology continues to advance, so should our approaches to PCB disposal, ensuring a balance between electronic innovation and ecological stewardship. Latest news
Troubleshooting Common Eddy Separator Problems
NewsJul.04,2025
The Role of Metal Recycling Plants in Circular Economy
NewsJul.04,2025
The Impact of Recycling Line Pickers on Waste Management Costs
NewsJul.04,2025
Safety Features Every Metal Shredder Should Have
NewsJul.04,2025
How Industrial Shredders Improve Waste Management Systems
NewsJul.04,2025
How Cable Granulators Contribute to Sustainable Recycling
NewsJul.04,2025